
Angiography: Type of X-ray Used to Check Blood Vessels
Angiography is a medical procedure that involves injecting a contrast dye into blood vessels and using X-rays to create images of the blood vessels, helping doctors diagnose and treat conditions like blockages or aneurysms.
What is Angiography
Angiography is a medical procedure.
- It's used to visualize blood vessels in the body.
- Typically performed in a specialized room.
- A contrast dye is often injected into blood vessels.
- X-ray technology captures images of the dye as it flows.
- Helps diagnose blockages, aneurysms, and other vascular issues.
- Essential for planning treatments like stent placement.
Angiography
Here are the basic details for the Angiography .
| Also Known As | Angiogram |
| Type | Diagnostic Imaging |
| Purpose | Visualize blood vessels, detect blockages |
| Preparation | Overnight fasting, medical history |
| Fasting | Typically required |
| Gender | All genders |
| Age Group | Adults |
| Procedure Duration | 30 minutes to several hours |
| Reporting Time | Typically within a few hours |
| Cost | 8,000 - 40,000* INR |
| Pregnancy Consideration | Caution during pregnancy |
| Risks and Safety | Minimal risks, contrast allergy risk |
| Accessibility | Available in specialized centers |
*Price range may vary as per location, facility, type, and procedure.
What are the Purpose or Reasons for Angiography?
Here are common reasons for Angiography.
- Visualize blood vessels and arteries
- Detect and locate blockages or narrowing
- Guide treatment of vascular conditions
- Evaluate coronary artery health (coronary angiography)
- Assess blood flow to organs and tissues
- Diagnose and plan treatment for aneurysms
- Investigate causes of unexplained pain or symptoms

Types of Angiography
Here are the types of angiography along with their primary use.
| Angiography Type | Organ/System | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic Angiography | Blood vessels | Evaluate blood vessel abnormalities |
| Coronary Angiography | Heart | Assess coronary artery blockages |
| Cerebral Angiography | Brain | Examine brain blood vessels |
| Peripheral Angiography | Extremities | Visualize peripheral blood vessels |
| Pulmonary Angiography | Lungs | Assess pulmonary artery condition |
| Renal Angiography | Kidneys | Evaluate renal artery abnormalities |
| Aortic Angiography | Aorta | Examine the aorta and its branches |
| Cardiac Catheterization | Heart | Guide cardiac interventions |
These angiography types serve diverse diagnostic purposes across different organ systems.
Preparing for Your Angiography: Tips and Information
Here is the basic preparation before, during, and after Angiography for any patient.
Before Angiography:
- Consultation: Schedule the angiography procedure and discuss your medical history, allergies, and any concerns with your healthcare provider.
- Fasting: Follow fasting instructions provided by your healthcare team, often requiring you to avoid food and liquids for a specific duration before the procedure.
- Medications: Inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking. Some may need to be adjusted or temporarily stopped, especially blood-thinning medications.
- Allergies: If you have known allergies to contrast dye or iodine, communicate this to your healthcare provider beforehand.
- Clothing: Wear comfortable clothing and avoid jewelry or accessories. You may be asked to change into a hospital gown.
During Angiography:
- Preparation: You'll be positioned on the angiography table, and the area where the catheter will be inserted (often in the groin or wrist) will be cleaned and numbed.
- Contrast Dye: Contrast dye is injected through the catheter to make blood vessels visible on X-ray images. You may feel a warm sensation when the dye is injected.
- Monitoring: Vital signs will be monitored throughout the procedure, and you may be asked to report any sensations or discomfort.
- Remain Still: It's crucial to stay as still as possible during the procedure to obtain clear images.
After Angiography:
- Recovery: After the procedure, you'll be monitored for a few hours. Rest and avoid strenuous activities for the remainder of the day.
- Hydration: Drinking fluids can help flush the contrast dye from your system. Follow any hydration recommendations from your healthcare team.
- Results: Your angiography results will be reviewed by a specialist, and a report will be sent to your healthcare provider.
- Follow-Up: Schedule a follow-up appointment with your healthcare provider to discuss the angiography results and any further steps or treatments if needed.
Note that specific instructions and procedures may vary depending on the type of angiography and your individual medical condition. Always follow the guidance provided by your healthcare team for a successful and safe angiography procedure.
Who Performs a Angiography?
| Professional | Role |
|---|---|
| Interventional Radiologist | Performs angiography procedures. |
| Radiologic Technologist | Assists during the procedure and operates equipment. |
| Radiology Nurse | Assists with patient care during angiography. |
Angiography Procedure
The procedure for Angiography typically follows these steps:
- Check-in and registration at the angiography department.
- You'll change into a hospital gown and remove any jewelry or metal objects.
- An intravenous (IV) line may be inserted to provide medications and fluids.
- You'll lie on an examination table, usually flat on your back.
- Sterile drapes are used to maintain a sterile field around the area of interest.
- Local anesthesia is applied to numb the insertion site, often in the groin or wrist.
- A catheter (thin, flexible tube) is inserted into an artery through a small incision.
- Contrast dye is injected through the catheter to visualize blood vessels on X-ray.
- Continuous X-ray images are taken as the dye flows through the blood vessels.
- The procedure may involve different angles and positions.
- You may be asked to hold your breath or make specific movements.
- The duration of the procedure varies but typically takes 30 minutes to a few hours.
- After the procedure, the catheter is removed, and pressure is applied to the insertion site to prevent bleeding.
- You'll be monitored for a short time before discharge.
- The images are interpreted by an interventional radiologist or vascular surgeon.
- You may receive the results during your visit or at a later time.
Angiography Results
Here are some common elements you might find in a Angiography report:
| Angiography Findings | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Blood Vessels Examined | Normal or Abnormal |
| Specific Vessel Observations | Description of any abnormalities, such as blockages, stenosis, aneurysms, or vascular malformations |
| Blood Flow Assessment | Evaluation of blood flow, velocity, andection |
| Use of Contrast Material | Details about the use of contrast agents, if applicable |
| Impression | Summary of key findings or diagnostic impressions |
| Recommendations | Follow-up tests, treatments, or interventions, if necessary |
| Conclusion | Final remarks or clinical recommendations |
Angiography is a dynamic imaging technique used to visualize blood vessels, and the results are typically discussed with the healthcare provider during or immediately after the procedure. Any abnormal findings would be addressed promptly, and appropriate next steps would be determined based on the clinical context.
Angiography Abnormal Results
Here is potential causes of abnormal angiography results:
| Abnormal Angiography Finding | Potential Causes |
|---|---|
| Vascular Narrowing (Stenosis) | Atherosclerosis, plaque buildup, vasculitis |
| Blocked Blood Vessel | Thrombosis, embolism, arterial dissection |
| Aneurysm | Weakening of the blood vessel wall, congenital abnormalities |
| Vascular Malformation | Congenital malformations, arteriovenous malformations |
| Abnormal Blood Flow | Vascular obstruction, shunts, collateral vessels |
| Contrast Extravasation | Vascular injury, rupture, or leakage |
Abnormal angiography findings can have various causes, and further evaluation and management depend on the specific findings and the patient's clinical condition. These results are typically interpreted by a vascular specialist or interventional radiologist who can determine the appropriate course of action.
How Long Does an Angiography Take?
The duration of an angiography procedure can vary depending on the specific type of angiography and the complexity of the examination. Here's a general overview of the approximate time it takes for different types of angiography procedures:
| Angiography Procedure | Duration |
|---|---|
| Diagnostic Angiography | 30 minutes to 1 hour |
| Coronary Angiography | 30 minutes to 1 hour |
| Cerebral Angiography | 1-2 hours |
| Peripheral Angiography | 30 minutes to 1 hour |
| Pulmonary Angiography | 30 minutes to 1 hour |
| Renal Angiography | 30 minutes to 1 hour |
| Aortic Angiography | 30 minutes to 1 hour |
| Cardiac Catheterization | 1-2 hours (including angiography) |
- Please note that these are approximate times and can vary based on factors such as the complexity of the blood vessel network being examined, the patient's specific condition, and the need for additional procedures during angiography.
- Additionally, some angiography procedures may require sedation or anesthesia, which can extend the total procedure time.
- Always follow the guidance provided by your healthcare provider for your specific angiography procedure.
Angiography Report
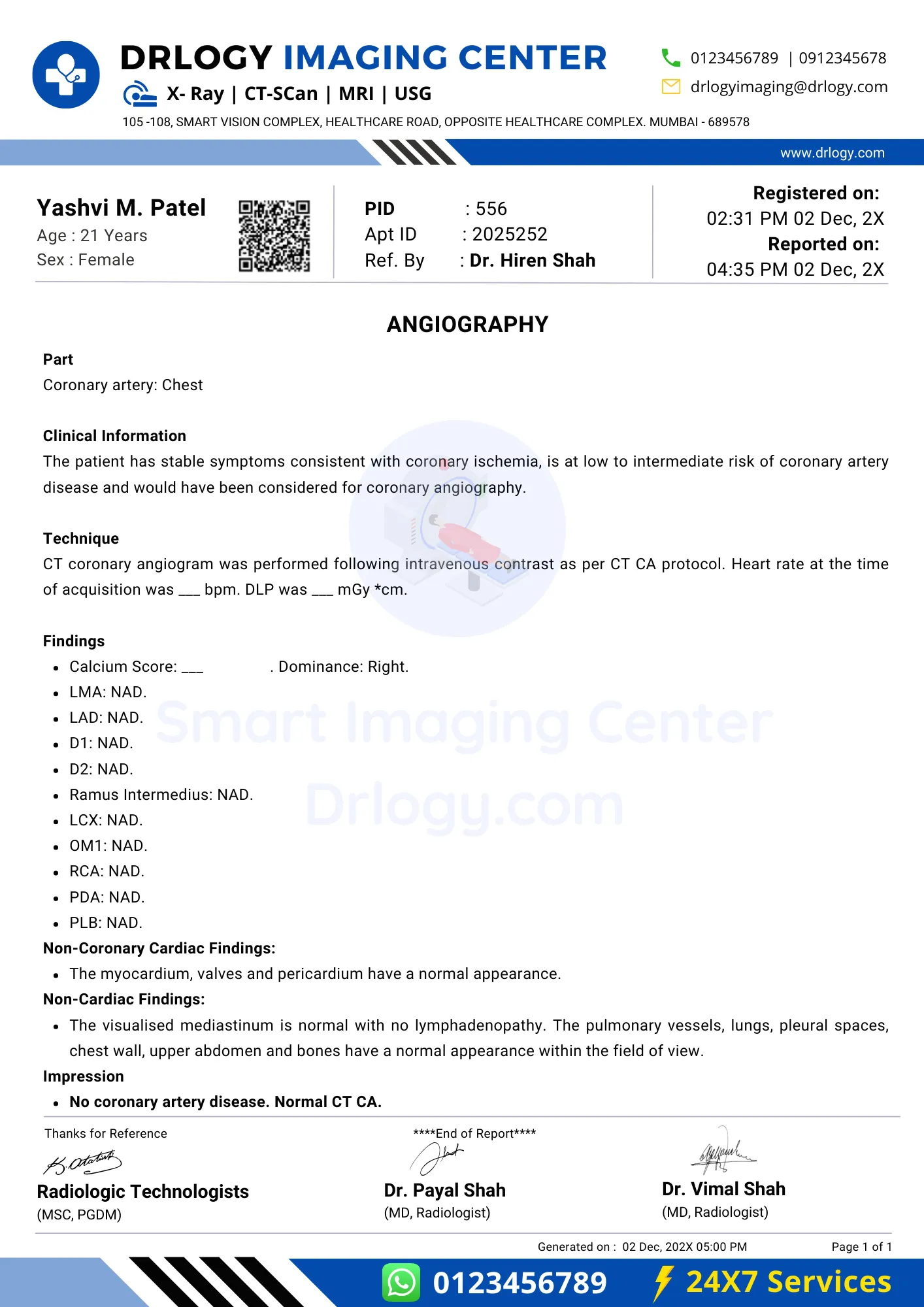
Angiography Limitation
Here are some limitation associated with a Angiography.
- Invasive procedure
- Risk of bleeding and infection
- Exposure to contrast dye
- Requires specialized equipment and expertise
- Limited to vascular imaging
Angiography Risk Factors
Here are some risk factors associated with a Angiography
- Exposure to ionizing radiation
- Potential for radiation-induced tissue damage
- Allergic reactions to contrast dye
- Risk of blood vessel damage during catheter insertion
- Minimal discomfort during the procedure
- Operator expertise crucial for safety
- Special precautions for pregnant individuals
Exploring the Safety of Angiography: Myth vs Reality
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| High radiation risk | Controlled exposure |
| Unsafe for all ages | Used with precautions |
| Painful procedure | Generally well-tolerated |
| Dangerous for heart | Commonly used in cardiac |
| Permanent damage | Short-term radiation |
| Risky for everyone | Risk assessment done |
| No operator error | Operator skill crucial |
Angiography Price
Here are the estimated Angiography Price in India with different top cities:
| City | Price Range (INR)* |
|---|---|
| Mumbai | 8,000 - 40,000 |
| New Delhi | 9,000 - 40,000 |
| Bangalore | 8,000 - 40,000 |
| Hyderabad | 9,000 - 40,000 |
| Kolkata | 8,000 - 40,000 |
| Pune | 9,000 - 40,000 |
| Lucknow | 8,000 - 40,000 |
| Noida | 9,000 - 40,000 |
| Surat | 9,000 - 40,000 |
| Gurugram | 8,000 - 40,000 |
| Patna | 8,000 - 40,000 |
| Chennai | 9,000 - 40,000 |
| Jaipur | 9,000 - 40,000 |
| Ahmedabad | 8,000 - 40,000 |
*Prices are approximate and range may vary as per location, facility, type, and procedure.
Summary
Overall, Angiography is a vital diagnostic tool for visualizing blood vessels and guiding medical interventions with controlled radiation exposure and operator expertise. Also check Drlogy Test for detailed information about all medical tests for patients, doctors, scholers and medical students.
Reference




