
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH) Calculator
The mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) is a measure of the average amount of hemoglobin in each red blood cell.
MCH Calculator
- The mean corpuscular hemoglobin calculator or MCH determines the average weight of Hb in the erythrocytes as MCH is one of the RBC indices.
- It is typically reported in picograms (pg).
- To calculate MCH, you need to know the hemoglobin level and the red blood cell count.
How To Calculate MCH
- Select Gender Male or Female
- Enter Hemoglobin Value in g/dL
- Enter RBC count in million cells/mcL
- Calculate MCH Value
MCH Normal Range Parameter
MCH Normal values for the above parameters can be found in the table below:
| Parameter | Normal range |
| Hemoglobin | 12 – 18 g/dL |
| RBC | 4.2 – 6.3 million cells/mcL |
| MCH | 27 – 33 pg |
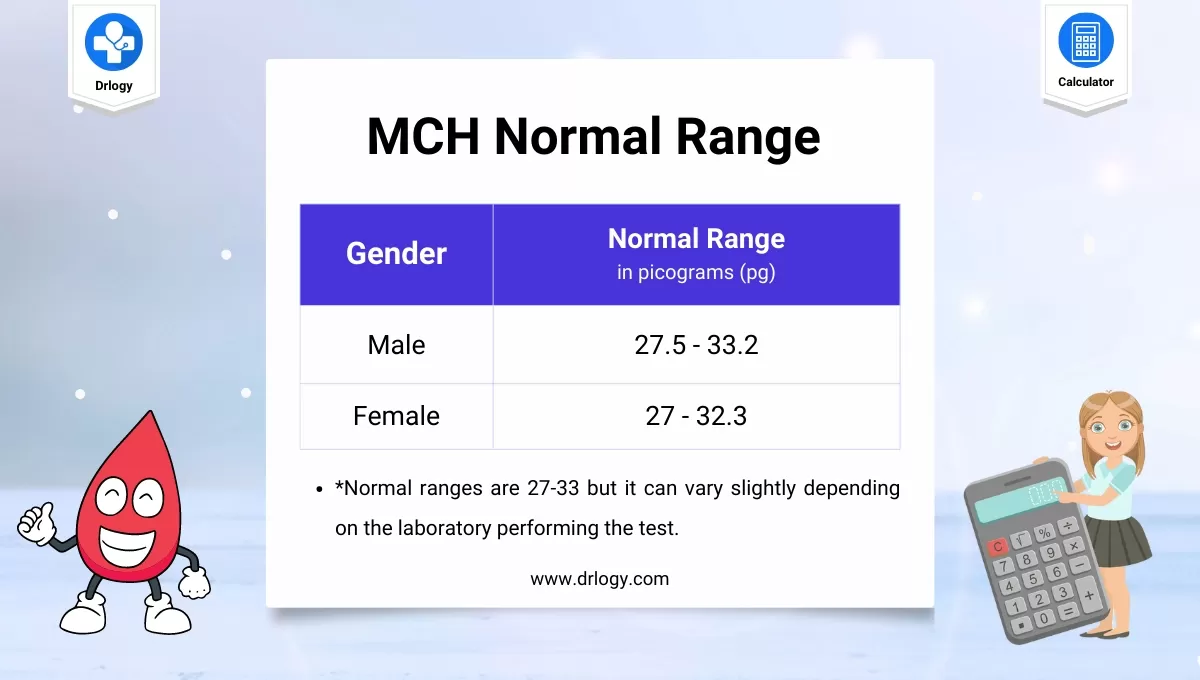
MCH Normal Range
The normal range of MCH in males and female are given below.
| Gender | Normal Range in picograms (pg) |
| Male | 27.5 - 33.2 |
| Female | 27 - 32.3 |
MCH Interpretation
Here's a table that can help with interpreting MCH values:
| MCH Value (pg) | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| < 27 | Low (hypochromic) |
| 27 - 33 | Normal |
| > 33 | High (hyperchromic) |
The interpretation of MCH values may vary depending on the individual's medical history, symptoms, and other factors. Your healthcare provider is best equipped to interpret your MCH value and determine any necessary next steps.
High MCH
A high MCH (mean corpuscular hemoglobin) value indicates that there is an excess amount of hemoglobin in each red blood cell. There are several possible causes of a high MCH value, including:
- Vitamin B12 or folate deficiency
- Alcoholism
- Liver disease
- Hypothyroidism
- Hemolytic anemia
- Certain medications
Low MCH
A low MCH (mean corpuscular hemoglobin) value indicates that there is a lower-than-normal amount of hemoglobin in each red blood cell. There are several possible causes of a low MCH value, including:
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Thalassemia
- Anemia of chronic disease
- Lead poisoning
- Bone marrow disorders
- Chronic kidney disease
Interesting Facts About MCH
- The concept of MCH was first introduced in the 1920s, to know the relationship between hemoglobin levels and red blood cell size. The term "mean corpuscular hemoglobin" was coined in the 1940s.
- MCH is often used in conjunction with other measures of blood health to diagnose and monitor various conditions, including anemia, sickle cell disease, and thalassemia.
- MCH is not a standalone test, and should always be evaluated in the context of other blood tests and medical history.
- MCH is typically measured as part of a complete blood count (CBC) test, which is a common blood test that evaluates a variety of blood components.
- The level of MCH can be affected by a variety of factors, including age, sex, genetics, and overall health status.
- MCH levels can be increased by smoking, alcohol consumption, and exposure to environmental toxins.
- MCH levels can be decreased by certain medications, including chemotherapy drugs and anticonvulsants.
MCH Calculator Benefits
The MCH (mean corpuscular hemoglobin) calculator can be a helpful tool for both healthcare providers and patients. Here are some potential benefits of using the MCH calculator:
- Quick and easy calculation: The MCH calculator can quickly calculate MCH values from hemoglobin and red blood cell count results, which can save time and reduce the risk of calculation errors.
- Assessment of anemia types: The MCH value can help differentiate between different types of anemia, such as iron-deficiency anemia or thalassemia.
- Monitoring treatment: For individuals with anemia, monitoring MCH values over time can help healthcare providers assess the effectiveness of treatment.
- Early detection of underlying health conditions: Abnormal MCH values may indicate an underlying health condition, such as a vitamin deficiency or bone marrow disorder, which can be detected early with regular blood tests.
- Patient education: Patients can use the MCH calculator to better understand their blood test results and the potential implications for their health.
Summary
Overall, the MCH calculator can be a useful tool in the diagnosis and management of various health conditions. However, it's important to note that the MCH value should always be interpreted in conjunction with other blood test results and a thorough medical evaluation. Check More Medical Health Related Calculator on Drlogy Calculator to get exact health solution.
Reference
- Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin [1].
- Beyan C, Kaptan K, Beyan E, Turan M. The platelet count/mean corpuscular hemoglobin ratio distinguishes combined iron and vitamin B12 deficiency from uncomplicated iron deficiency. Int J Hematol. 2005; 81(4):301-3 [2].
FAQ
What is MCH formula?
The MCH (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin) is the average amount of hemoglobin in a single red blood cell and is calculated using the following formula:
MCH = (Hemoglobin ÷ Red Blood Cell Count) x 10
Where Hemoglobin is measured in grams per deciliter (g/dL) and Red Blood Cell Count is measured in millions per microliter (million/μL).
What is the normal range for MCH formula?
- The normal range for MCH is typically between 27-33 picograms (pg) per red blood cell.
- However, the normal range may vary slightly between different laboratories and may depend on factors such as age and sex.
What does low MCH mean?
Low MCH (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin) means that the average amount of hemoglobin in each red blood cell is lower than normal.
- This could indicate various medical conditions such as iron deficiency anemia, thalassemia, chronic diseases, or other nutritional deficiencies.
- A healthcare provider should be consulted to determine the underlying cause of low MCH and appropriate treatment.




