
Daily Water Intake Calculator For Min Water Your Body Needs
Daily Water Intake Calculator
kg
Result
What is Daily Water Intake Calculator
- Use this hydration calculator to easily calculate the recommended daily water intake you need to keep yourself healthy and at peak physical and mental performance.
- If you are asking yourself how much water should you drink per day our water calculator will calculate that for you.
Steps To Calculate Daily Water Intake
- Enter Your Age
- Enter Your Weight
- Enter Your Activity
- Calculate Your Daily Water Intake
Daily Water Intake
- Getting enough water every day is important for your health.
- Drinking water can prevent dehydration, a condition that can cause unclear thinking, result in mood change, cause your body to overheat, and lead to constipation and kidney stones.
- Water has no calories, so it can also help with managing body weight and reducing calorie intake when substituted for drinks with calories, such as sweet tea or regular soda.
Water helps your body:
- Keep a normal temperature.
- Lubricate and cushion joints.
- Protect your spinal cord and other sensitive tissues.
- Get rid of waste through urination, perspiration, and bowel movements.
Your body needs more water when you are:
- In hot climates.
- More physically active.
- Running a fever.
- Having diarrhea or vomiting.
Tips to Drink More Water
- Carry a water bottle with you and refill it throughout the day.
- Freeze some freezer-safe water bottles. Take one with you for ice-cold water all day long.
- Choose water over sugary drinks.
- Opt for water when eating out. You’ll save money and reduce calories.
- Serve water during meals.
- Add a wedge of lime or lemon to your water. This can help improve the taste.
Recommended Water Intake
In the table, recommended water intake is in L/day (litre or liter per day). For reference, one liter is approximately equal to four standard water glasses.
| Age group | ESFA | IOM | ||
| Water intake | Fluid intake | Water intake | Fluid intake | |
| 0-6 mo. | 0.68 (milk) | 0.68 (milk) | 0.70 | 0.70 |
| 6-12 mo. | 0.80 - 1.00 | 0.64 - 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| 1-2 years | 1.10 - 1.20 | 0.88 - 0.90 | N/A | N/A |
| 2-3 years | 1.30 | 1.00 | N/A | N/A |
| 1-3 years | N/A | N/A | 1.30 | 0.90 |
| 4-8 years | 1.60 | 1.20 | 1.70 | 1.20 |
| 9-13 y. Boys | 2.10 | 1.60 | 2.40 | 1.80 |
| 9-13 y. Girls | 1.90 | 1.50 | 2.10 | 1.60 |
| Boys 14+ & Adult Men | 2.50 | 2.00 | 3.30 | 2.60 |
| Girls 14+ & Adult Women | 2.00 | 1.60 | 2.30 | 1.80 |
| Pregnant Women | 2.30 | 1.84 | 2.60 | 1.90 |
| Lactating Women | 2.60 | 2.10 | 3.40 | 2.80 |
| Elderly | As adults | As adults | As adults | As adults |
Daily Water Intake
Here is the average daily water intake ended water intake table as per date.
| Body Weight (Pounds) | Daily Water Intake (ounces) | Body Weight (Kg) | Daily Water Intake (gm) |
| 100 | 67 | 45 | 1899 |
| 110 | 74 | 50 | 2098 |
| 120 | 80 | 54 | 2268 |
| 130 | 87 | 59 | 2466 |
| 140 | 94 | 64 | 2665 |
| 150 | 100 | 68 | 2835 |
| 160 | 107 | 73 | 3033 |
| 170 | 114 | 77 | 3232 |
| 180 | 121 | 82 | 3430 |
| 190 | 127 | 86 | 3600 |
| 200 | 134 | 91 | 3799 |
| 210 | 141 | 95 | 3997 |
| 220 | 148 | 100 | 4196 |
| 230 | 154 | 104 | 4366 |
| 240 | 161 | 109 | 4564 |
| 250 | 168 | 113 | 4763 |
Benefits of drinking enough daily water
- Water is essential for our bodies to function correctly and efficiently.
- It’s vital to our health and can have a huge impact on our overall health and wellness.
- Most of us know this, but do you actually know why water is so important?
Here are the main benefits of staying hydrated:
- It Aids digestion and prevents constipation
- Carries oxygen and nutrients to your cells
- Helps stabilize blood pressure and heartbeat
- Supports healthy joints and joint function
- It helps regulate body temperature
- Potentially lowers the risk for disease in the future such as cancer, heart disease, high blood pressure, kidney stones, and stroke.
How much water should I drink to try and lose weight?
- Let’s start out by being clear that drinking water alone will likely not lead to weight loss.
- However, the benefits of drinking water can help support and encourage weight loss.
- First, water helps us to feel full and satiated.
- When we are hydrated, we tend to eat less since we don’t confuse signs of dehydration with signs of hunger.
- Many people actually report feeling hungry when they are in fact dehydrated.
- Another added benefit of drinking water is that it is less likely that someone will overeat.
- When your stomach is filled with liquid from drinking water, you will less likely to eat too much or mindlessly snack throughout the day.
- Lastly, if you are focused on drinking more water, you are less likely to reach for sugary drinks and beverages with empty calories.
- Swapping in water for higher calorie beverages is a great way to lose weight.
Signs of Dehydration
Signs of mild dehydration to watch out for can include:
- Thirst
- Not peeing
- Dark yellow urine
- Dry skin
- Feeling dizzy
- Lack of energy
Water Content in Foods
Below is a reference table for the water content in selected foods.
| Water percentage | Food item |
| 100% | Water |
| 90-99% | Fat-free milk, cantaloupe, strawberries, watermelon, lettuce, cabbage, celery, spinach, pickles, squash (cooked) |
| 80-89% | Fruit juice, yogurt, apples, grapes, oranges, carrots, broccoli (cooked), pears, pineapple |
| 70-79% | Bananas, avocados, cottage cheese, ricotta cheese, potato (baked), corn (cooked), shrimp |
| 60-69% | Pasta, legumes, salmon, ice cream, chicken breast |
| 50-59% | Ground beef, hot dogs, feta cheese, tenderloin steak (cooked) |
| 40-49% | Pizza |
| 30-39% | Cheddar cheese, bagels, bread |
| 20-29% | Pepperoni sausage, cake, biscuits |
| 10-19% | Butter, margarine, raisins |
| 1-9% | Walnuts, peanuts (dry roasted), chocolate chip cookies, crackers, cereals, pretzels, taco shells, peanut butter |
| 0% | Oils, sugars |
Benefits of Staying optimally Hydrated
One of the reasons to use a hydration calculator is to maintain a healthy life, but scientific studies also link adequate water intake to benefits for the treatment of health conditions as well as mental state improvement.
Water comprises from 75% body weight in infants to 55% in the elderly and is essential for cellular homeostasis and life so it is no wonder water is so important to one's health.
Kidney health
- The kidneys function more efficiently in the presence of an abundant water supply.
- If the kidneys economize on water, this results in producing more concentrated urine which comes at a greater cost in energy and more wear on their tissues.
- This is especially likely to occur when the kidneys are under stress, for example when the diet contains excessive amounts of salt or toxic substances that need to be eliminated.
- Consequently, drinking enough water helps protect this vital organ.
- There is strong evidence that the recurrence of kidney stones is much less likely when your hydration status is good due to the increased urine volume.
- So, there is your first reason for using a daily water intake calculator to estimate how much water you need to drink per day.
Sports performance
- During challenging athletic events, it is not uncommon for athletes to lose 6–10% of body weight in sweat loss, thus leading to dehydration if fluids have not been adequately replenished.
- Decrements in physical performance in athletes have been observed under much lower levels of dehydration: as little as 2% Under relatively mild levels of dehydration, individuals engaging in rigorous physical activity will experience decrements in performance related to reduced endurance, increased fatigue, altered thermoregulatory capability, reduced motivation, and increased perceived effort.
- Rehydration can reverse these deficits, and also reduce oxidative stress induced by exercise and dehydration.
- Hypohydration appears to have a more significant impact on high-intensity and endurance activities such as tennis and long-distance running than on anaerobic activities such as weight lifting or on shorter-duration activities, such as rowing.
- Children are especially prone to voluntary dehydration so child athletes and children doing sports in hot climates should start well-hydrated every day to avoid any potential issues.
Cognitive abilities
- A body of studies examined by Popkin et. indicates that low to moderate dehydration may negatively affect cognitive performance.
- Rather than indicating that the effects of hydration or water ingestion on cognition are contradictory, many of the studies differ significantly in methodology and in the measurement of cognitive behaviors.
- Most studies in which dehydration was induced by combined heat and exercise, thus it is difficult to disentangle the effects of dehydration on cognitive performance in temperate conditions from the effects of heat and exercise.
- In practice, relatively little is known about the mechanism of mild dehydration’s effects on mental performance. It has been proposed that mild dehydration acts as a physiological stressor which competes with and draws attention from cognitive processes.
- However, research on this hypothesis is limited and merits further exploration.
- A more recent study by Riebl S. K. and Davy B. M. came to the conclusion that even though traditionally a 2% or more body water deficit was thought to produce cognitive performance decrements more recent literature suggests that even mild dehydration – a body water loss of 1–2% – can impair cognitive performance.
- Counseling clients about their health and well-being should include conveying the importance of water for normal body functioning, as well as its effects on physical and cognitive performance.
- It would therefore seem that getting close to your optimal hydration level with the help of a hydration calculator can have benefits for your mental power.
Headache prevention and treatment
- A 2012 randomized control trial by Spigt et. suggests that considering the observed positive subjective effects, it seems reasonable to recommend headache patients to try this non-invasive intervention for a short period of time to see whether they experience improvement.
Type II Diabetes
- Epidemiological research has demonstrated that low daily total water intake is associated with increased diagnosis of hyperglycemia
- A study confirms that 3 days of low total water intake in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus acutely impairs blood glucose response during an oral glucose tolerance test via cortisol but not RAAS-mediated glucose regulation, where RAAS stands for the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Constipation and water intake
- Constipation, characterized by slow gastrointestinal transit, small, hard stools, and difficulty in passing stool, has a number of causes including medication use, inadequate fiber intake, poor diet, and illness.
- Inadequate fluid consumption is touted as a common culprit in constipation and increasing fluid intake is a frequently recommended treatment.
- However, the evidence suggests that increasing fluids is only of usefulness in individuals in a hypohydrated state and is of little utility in properly hydrated people.
- In young children with chronic constipation, increasing daily water intake by 50% did not affect constipation scores.
Heart rate and blood pressure
- Water intake acutely reduces heart rate and increases blood pressure in people with normal or increased blood pressure.
- The effects of water intake on the pressor effect and heart rate occur within 15–20 minutes of drinking water and can last for up to 60 minutes.
- Water ingestion is also beneficial in preventing vasovagal reaction with syncope in blood donors at high risk for post-donation syncope.
- Some strong reasons to consider using a water intake calculator and to adhere to the estimate as best as one can.
Bronchopulmonary disorders
- There is strong evidence from meta analyses of randomized controlled trials that exercise-related asthma is linked with low fluid intake.
- Thus, increasing water intake per day has a beneficial effect on the condition.
Skin and skin conditions
- There is no evidence to support the notion that drinking more water will improve the skin complexion, remove wrinkles, and acne, or help with other skin conditions.
- Increasing the amount of water intake per day will improve the skin thickness and density in persons with low initial water intake.
- But if you are already drinking adequate amounts of water every day, increasing that will not be beneficial for your skin.
All-risk mortality
- Proper water intake appears to have certain benefits they may not go as far as increasing your lifespan.
- However, it is unclear what size of effect the study was powered to exclude.
- While all-risk mortality is an important measurement, quality of life and achievements should be taken into account when considering the usefulness of knowing how much water you need to drink and of abiding by those recommendations.
Summary
Overall daily water intake calculator will give you min amount of daily water quantity that you should take to stay healthy. Check More Medical Health Related Calculator on Drlogy Calculator to get exact health solutions.
Reference
FAQ
How do you calculate total body water?
Formula For Calculating Total Body water for male and female are :
- Male TBW = 2.447 - (0.09156 x age) + (0.1074 x height) + (0.3362 x weight)
- Female TBW = -2.097 + (0.1069 x height) + (0.2466 x weight)
How many liters is total body water?
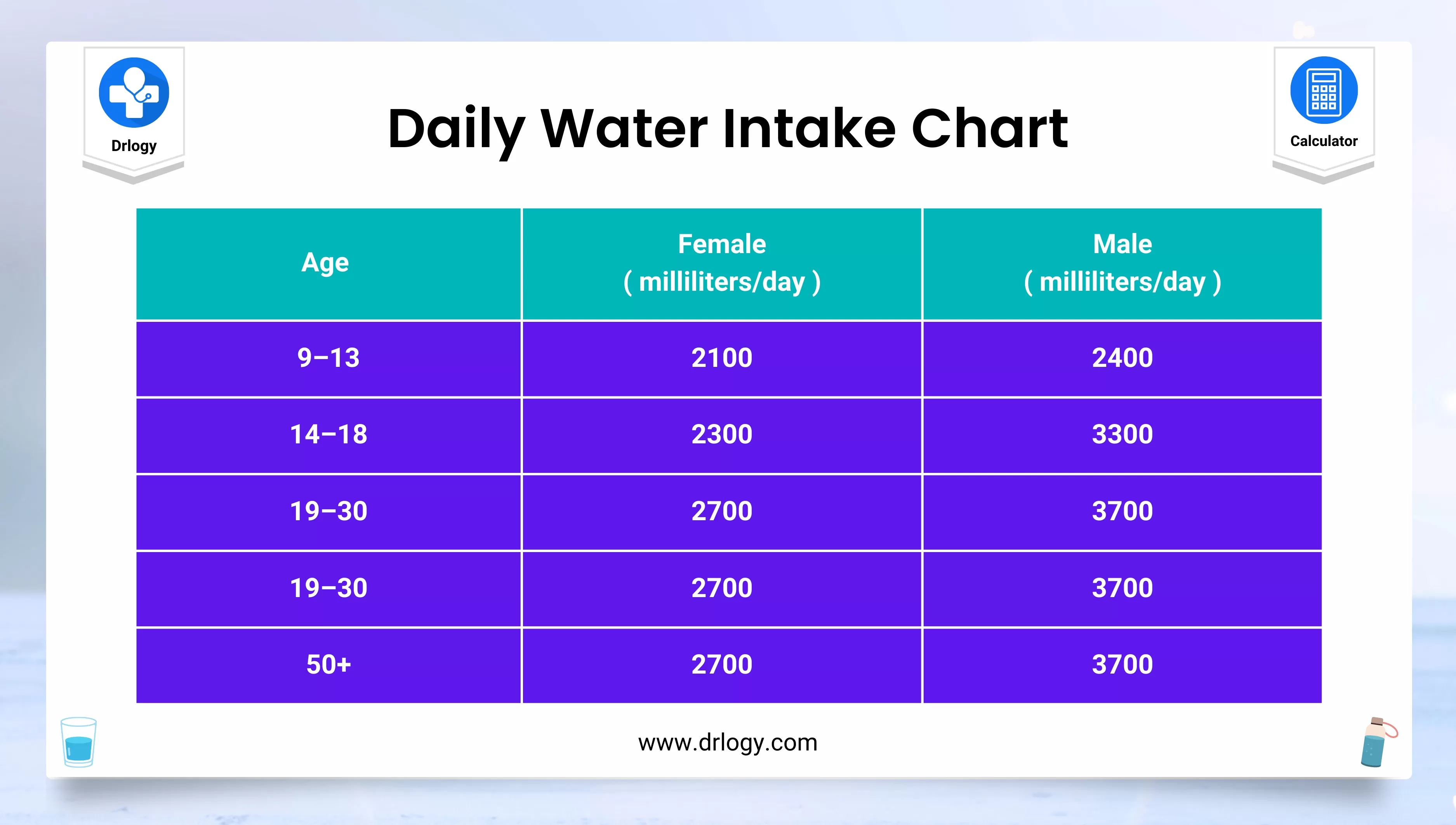
Here are agewise total body water intake is given.
|
Age |
Recommended total body water (milliliters per day) |
|
0–6 months |
700 |
|
6–12 months |
800 |
|
1–2 years |
1,300 |
|
4–8 years |
1,700 |
|
9–13 years (males) |
2,400 |
|
9–13 years (females) |
2,100 |
|
14–18 years (males) |
3,300 |
|
14–18 years (females) |
2,300 |
|
Adult male |
3,700 |
|
Adult female |
2,700 |
|
During pregnancy |
3,000 |
|
While breastfeeding |
3,800 |
How much water is too much?
Many people wonder if there is actually a point where you can drink too much water. There are some rare cases of someone over-hydrating, known as hyponatremia. However, it is very rare and usually only seen in endurance athletes who are over-drinking while doing very intense exercise or in older adults with certain health conditions.




